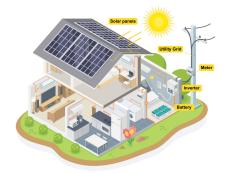
Solar Electric Systems
Solar electric systems, also known as photovoltaic (PV) systems, capture sunlight and convert it into electricity for use in homes and businesses. PV systems allow homeowners to produce the energy needed to power all or some of their home from a clean, renewable source.
A PV system can be on-grid—connected to the region's electrical power grid — or off-grid — a stand-alone system that supplies only the individual home. On-grid PV systems draw power from the local utility company if need be and feed excess energy that's generated but not used by the household to the utility company. Federal law requires the local utility to buy PV-generated electricity from homeowners. The rate paid for the electricity depends on the utility company. Some utilities offer net metering, which means the homeowner is paid the retail rate for electricity (the same rate that the homeowner would pay to buy electricity). Utilities that don't offer net metering buy PV-generated electricity from homeowners at a lower, wholesale rate.
On-grid PV systems have these components:
- Solar cells. These are the basic building blocks of the system. They're made of crystalline semiconductor materials, the most popular being silicon. Solar cells are combined to form solar panels that output 10 to 300 watts of electricity. Several panels can be combined to form an array positioned on or near the home. Ten to 20 arrays can provide enough power for a typical household.
- Inverter. An inverter converts direct-current (DC) electricity produced by solar cells to alternating-current (AC) electricity required to run household appliances. Additional conditioning equipment is needed to ensure that the quality of electricity produced meets the load requirements and utility-company standards.
- Meter. A meter allows homeowners to monitor the amount of power being consumed. If the utility company offers net metering, the meter can also be used to record excess electricity the PV system feeds back into the grid. In this case, the meter spins forward when electricity is being drawn and backward when electricity is being produced. Utilities that don't offer net metering require homeowners to install a second meter to track the electricity the PV system feeds into the grid.
Off-grid PV systems require the following additional components: batteries to store power for use when the system isn't producing electricity; charge controllers to regulate the electricity flowing from the generation source into the load or batteries; and safety features such as safety disconnects, grounding equipment and surge protectors.
The cost of a PV system depends on the size of the system. It has high upfront costs, but homeowners can benefit over the life of the system through reduced monthly electricity costs. A small, single-PV-panel system that produces 75 watts will cover only a small fraction of a typical home's electricity need. A 2-kilowatt system will meet nearly all the needs of an energy-efficient home. And a 5-kilowatt system will completely meet the energy needs of many conventional homes.
Regulations and permitting for a PV system vary widely. The system supplier or installer should know the requirements of the local community and utility company.